MiroTalk WEB - Self hosting
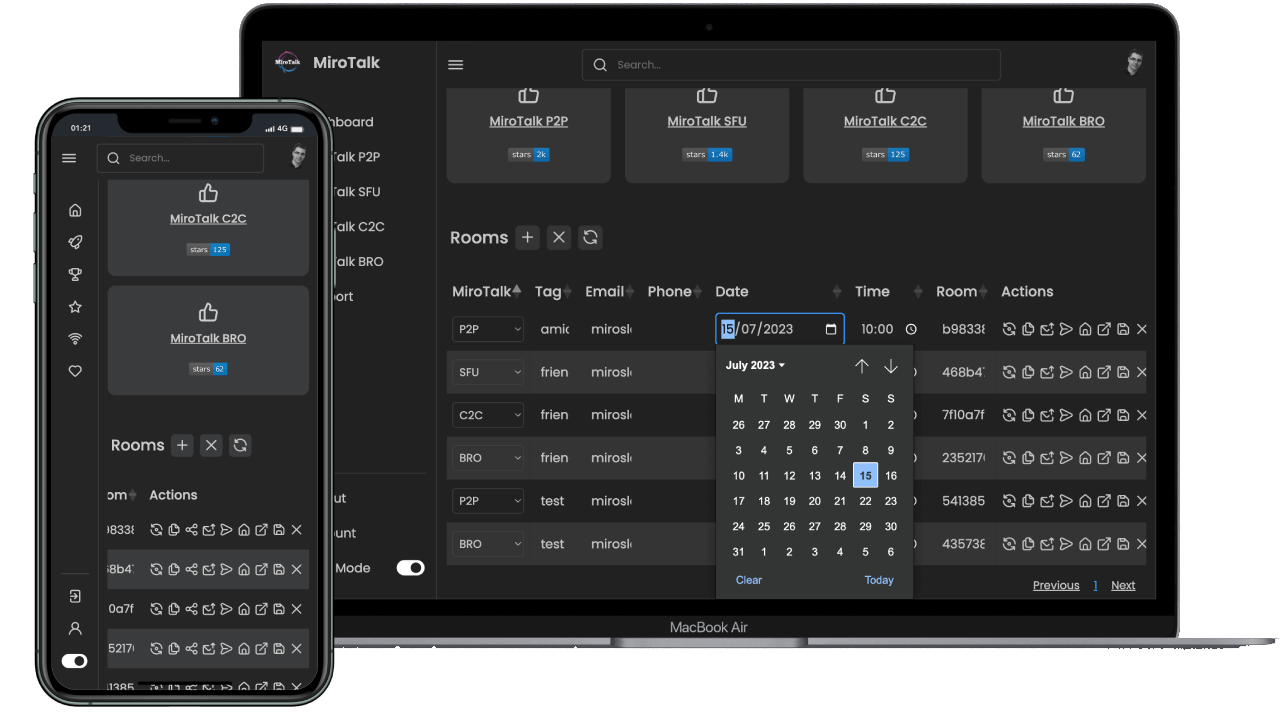
Description
MiroTalk WEB is a browser-based room scheduler for organizing and managing team meetings. Streamlines internal communication and collaboration for organizations.
Live demo: https://webrtc.mirotalk.com
Requirements
- Server Selection:
- OS: Ubuntu 22.04 LTS.
- Node.js (LTS) and npm
- Domain or Subdomain Name (e.g.,
YOUR.DOMAIN.NAME) with a DNS A record pointing to your server's IPv4 address.
Installation

Install NodeJS and npm using Node Version Manager
Quick start
# Clone the project repo
$ git clone https://github.com/miroslavpejic85/mirotalkwebrtc.git
# Go to project dir
$ cd mirotalkwebrtc
# Copy .env.template to .env and customize it according to your needs
$ cp .env.template .env
# Copy config.template.js to config.js and customize it according to your needs
$ cp backend/config.template.js backend/config.js
Config.js
Customize the backend/config.js according to your needs:
"use-strict";
module.exports = {
//...
MiroTalk: {
P2P: {
Visible: true,
Home: "https://P2P-DOMAIN-NAME",
Room: "https://P2P-DOMAIN-NAME/newcall",
Join: "https://P2P-DOMAIN-NAME/join/",
//...
},
SFU: {
Visible: true,
Home: "https://SFU-DOMAIN-NAME",
Room: "https://SFU-DOMAIN-NAME/newroom",
Join: "https://SFU-DOMAIN-NAME/join/",
//...
},
C2C: {
Visible: true,
Home: "https://C2C-DOMAIN-NAME",
Room: "https://C2C-DOMAIN-NAME/?room=",
//...
},
BRO: {
Visible: true,
Home: "https://BRO-DOMAIN-NAME",
Broadcast: "https://BRO-DOMAIN-NAME/broadcast?id=",
Viewer: "https://BRO-DOMAIN-NAME/viewer?id=",
//...
},
},
//...
};
Here's a breakdown of the structure:
Visible: Display on MiroTalk WEB dashboard (boolean).Home: Homepage URL.Room: URL for creating a new call/room.Join: URL for joining an existing call/room.Broadcast: URL for broadcasting.Viewer: URL for viewing a broadcast.
To use this configuration file, you would replace the placeholder values like 'https://P2P-DOMAIN-NAME' with the actual domain or subdomain names where your MiroTalk instances are hosted. This ensures that the application correctly generates the URLs for different MiroTalk functionalities.
For example, if your P2P instance is hosted at https://mirotalk-p2p.example.com, you would replace 'https://P2P-DOMAIN-NAME' with 'https://mirotalk-p2p.example.com' in the config.js file. Repeat this process for each component and its corresponding URLs.
MongoDb

Local MongoDB Deployment
Install Docker and Docker Compose:
# Install docker
$ sudo apt install -y docker.io
# Instal docker-compose
$ sudo apt install -y docker-compose
To run MongoDB locally with Docker Compose, you can use the following commands:
Start the MongoDB container:
Stop the MongoDB container:
Cloud MongoDB Deployment (Optional)
For cloud MongoDB deployments, such as with MongoDB Atlas, make sure to update the credentials in the `.env` file accordingly.
User Email Verification (Optional)

By default, email verification is disabled. To enable it, set EMAIL_VERIFICATION to true in the .env file, and ensure the email settings are properly configured.
Install dependencies and start the server
Check if is correctly installed: http://YOUR.DOMAIN.NAME:9000
Using PM2 (Process Manager)

Install PM2:
# Install pm2
$ npm install -g pm2
# Start the server
$ pm2 start backend/server.js --name mirotalkweb
# Takes a snapshot
$ pm2 save
# Add it on startup
$ pm2 startup
Using Docker

Install Docker and Docker Compose:
# Install docker
$ sudo apt install -y docker.io
# Install docker-compose
$ sudo apt install -y docker-compose
# Clone the project repo
$ git clone https://github.com/miroslavpejic85/mirotalkwebrtc.git
# Go to project dir
$ cd mirotalkwebrtc
# Copy env.template to .env and customize it according to your needs
$ cp .env.template .env
# Copy config.template.js to config.js and customize it according to your needs
$ cp backend/config.template.js backend/config.js
# Copy docker-compose.template.yml in docker-compose.yml and customize it according to your needs if needed
$ cp docker-compose.template.yml docker-compose.yml
# Pull the official Docker image
$ docker pull mirotalk/webrtc:latest
# Create and start containers (-d as daemon)
$ docker-compose up
Check if is correctly installed: https://YOUR.DOMAIN.NAME:9000
Configuring Nginx & Certbot

In order to use it without the port number and to have encrypted communications (mandatory to make it work correctly), we going to install nginx and certbot
# Install Nginx
$ sudo apt-get install -y nginx
# Install Certbot (SSL certificates)
$ sudo apt install -y snapd
$ sudo snap install core; sudo snap refresh core
$ sudo snap install --classic certbot
$ sudo ln -s /snap/bin/certbot /usr/bin/certbot
# Configure Nginx
$ sudo vim /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/default
Add the following:
# HTTP — redirect all traffic to HTTPS
server {
listen 80;
listen [::]:80;
server_name YOUR.DOMAIN.NAME;
return 301 https://$host$request_uri;
}
# Test Nginx configuration
$ sudo nginx -t
# Enable HTTPS with Certbot (follow the instruction)
$ sudo certbot certonly --nginx
# Add Let's Encrypt configuration to Nginx
$ sudo vim /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/default
Add the following:
# MiroTalk WebRTC admin - HTTPS — proxy all requests to the Node app
server {
# Enable HTTP/2
listen 443 ssl http2;
listen [::]:443 ssl http2;
server_name YOUR.DOMAIN.NAME;
# Use the Let’s Encrypt certificates
ssl_certificate /etc/letsencrypt/live/YOUR.DOMAIN.NAME/fullchain.pem;
ssl_certificate_key /etc/letsencrypt/live/YOUR.DOMAIN.NAME/privkey.pem;
location / {
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_pass http://localhost:9000/;
proxy_http_version 1.1;
proxy_set_header Upgrade $http_upgrade;
proxy_set_header Connection "upgrade";
}
}
# Test Nginx configuration again
$ sudo nginx -t
# Restart nginx
$ service nginx restart
$ service nginx status
# Set up auto-renewal for SSL certificates
$ sudo certbot renew --dry-run --cert-name YOUR.DOMAIN.NAME
# Show certificates
$ sudo certbot certificates
Check Your MiroTalk WEB instance: https://YOUR.DOMAIN.NAME
Apache Virtual Host (Alternative to Nginx)

If you prefer Apache, configure it with the equivalent settings provided in this guide.
# Install apache with certbot
$ apt install python3-certbot-apache -y
# Setting up ssl
$ certbot --apache --non-interactive --agree-tos -d YOUR.DOMAIN.NAME -m your.email.address
# Edit the apache sites
$ sudo vim /etc/apache2/sites-enabled/YOUR.DOMAIN.NAME.conf
Add the following:
# HTTP — redirect all traffic to HTTPS
<VirtualHost *:80>
ServerName YOUR.DOMAIN.NAME
Redirect permanent / https://YOUR.DOMAIN.NAME
</VirtualHost>
<VirtualHost *:443>
ServerName YOUR.DOMAIN.NAME
# SSL Configuration
SSLEngine on
SSLCertificateFile /etc/letsencrypt/live/YOUR.DOMAIN.NAME/fullchain.pem
SSLCertificateKeyFile /etc/letsencrypt/live/YOUR.DOMAIN.NAME/privkey.pem
Include /etc/letsencrypt/options-ssl-apache.conf
# Enable HTTP/2 support
Protocols h2 http/1.1
<Location />
# Proxy Configuration for Node.js App
ProxyPass http://localhost:9000/
ProxyPassReverse http://localhost:9000/
ProxyPreserveHost On
RequestHeader set X-Forwarded-For "%{REMOTE_ADDR}s"
RequestHeader set X-Forwarded-Proto "https"
RequestHeader set Host "%{HTTP_HOST}s"
# Enable WebSocket proxy support for Socket.IO
RewriteEngine On
RewriteCond %{HTTP:Upgrade} =websocket [NC]
RewriteRule /(.*) ws://localhost:9000/socket.io/$1 [P,L]
# Adjust the WebSocket path according to your Socket.IO configuration
# For Socket.IO 3.x or higher, use /socket.io/?EIO=4&transport=websocket
</Location>
</VirtualHost>
# Check configuration
sudo apache2ctl configtest
sudo a2enmod proxy # Enables the `mod_proxy` module, which is essential for proxying HTTP and WebSocket connections.
sudo a2enmod proxy_http # Enables the `mod_proxy_http` module, which adds support for proxying HTTP connections.
sudo a2enmod proxy_wstunnel # Enables the `mod_proxy_wstunnel` module, which provides support for tunneling WebSocket connections
# Restart apache
sudo systemctl restart apache2
Updating Your Instance
To keep your MiroTalk WEB instance up to date, create an update script:
For PM2:
For Docker:
#!/bin/bash
cd mirotalkwebrtc
git pull
docker-compose down
docker-compose pull
docker image prune -f
docker-compose up -d
Make the script executable
To update your MiroTalk WEB instance to the latest version, run the script:
Changelogs
Stay informed about project updates by following the commits of the MiroTalk WEB project here