Coturn STUN/TURN Server
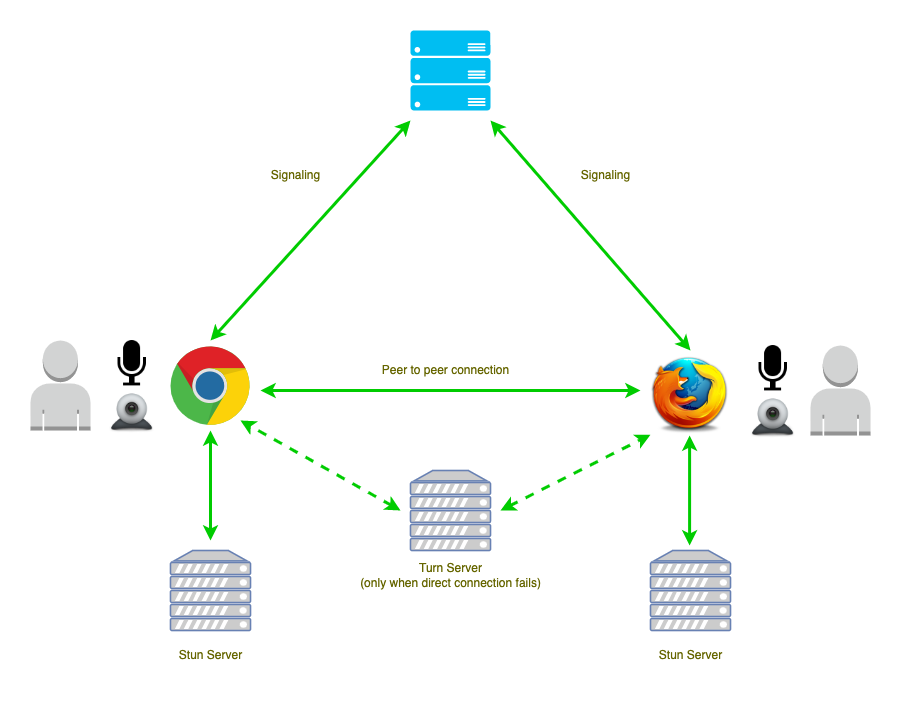
Requirements
- Server Selection:
- OS: Ubuntu 22.04 LTS.
- Domain or Subdomain Name (e.g.,
YOUR.DOMAIN.NAME) with a DNS A record pointing to your server's IPv4 address. - Certbot to generate
cert&pkeyfor/etc/turnserver.conf.
Installation
Install Coturn:
Install Certbot

Request SSL Certificate
Replace YOUR.DOMAIN.NAME with your real domain or subdomain name.
# The certificates can be found in /etc/letsencrypt/live/YOUR.DOMAIN.NAME/
$ sudo certbot certonly --standalone -d YOUR.DOMAIN.NAME
# Automatically renew the certificates
$ sudo certbot renew
# OR if you have running Nginx
$ sudo certbot renew --nginx
Turn_Server config
Open /etc/turnserver.conf and add the following by replacing YOUR.DOMAIN.NAME with your real domain or subdomain name.
For a full configuration example, see the official guide here
listening-port=3478
tls-listening-port=5349
min-port=10000
max-port=20000
fingerprint
lt-cred-mech
user=YOUR.USERNAME:YOUR.PASSWORD
server-name=YOUR.DOMAIN.NAME
realm=YOUR.DOMAIN.NAME
total-quota=500
stale-nonce=600
cert=/etc/letsencrypt/live/YOUR.DOMAIN.NAME/fullchain.pem
pkey=/etc/letsencrypt/live/YOUR.DOMAIN.NAME/privkey.pem
cipher-list="ECDHE-RSA-AES256-GCM-SHA512:DHE-RSA-AES256-GCM-SHA512:ECDHE-RSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384:DHE-RSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384:ECDHE-RSA-AES256-SHA384"
no-loopback-peers
no-multicast-peers
simple-log
Uncomment the following line to run Coturn as an automatic system service daemon in /etc/default/coturn
If you can't reach coturn on tls-listening-port, try to edit /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/coturn.service
Reload daemon:
Coturn commands
$ sudo service coturn status
$ sudo service coturn stop
$ sudo service coturn start
$ sudo service coturn restart
Using Docker

# Step 1: Pull the Coturn Docker image from Docker Hub (https://hub.docker.com/r/coturn/coturn)
$ docker pull coturn/coturn
# Step 2: Run a Coturn container in detached mode with host network mode
# and mount a local configuration file into the container
docker run -d \
--network=host \
--user root \
-v /etc/turnserver.conf:/etc/coturn/turnserver.conf \
-v /etc/letsencrypt/live/YOUR.DOMAIN.NAME/fullchain.pem:/etc/letsencrypt/live/YOUR.DOMAIN.NAME/fullchain.pem \
-v /etc/letsencrypt/live/YOUR.DOMAIN.NAME/privkey.pem:/etc/letsencrypt/live/YOUR.DOMAIN.NAME/privkey.pem \
coturn/coturn
Useful commands:
# List the currently running Docker containers
$ docker ps
# Stop the Coturn container with the name "compassionate_swanson"
$ docker stop compassionate_swanson
# Start the Coturn container with the name "compassionate_swanson"
$ docker start compassionate_swanson
Docker compose
If you prefer docker-compose.yml:
services:
coturn:
image: coturn/coturn
container_name: coturn
network_mode: "host"
user: "root"
restart: unless-stopped
volumes:
- /etc/turnserver.conf:/etc/coturn/turnserver.conf
- /etc/letsencrypt/live/YOUR.DOMAIN.NAME/fullchain.pem:/etc/letsencrypt/live/YOUR.DOMAIN.NAME/fullchain.pem
- /etc/letsencrypt/live/YOUR.DOMAIN.NAME/privkey.pem:/etc/letsencrypt/live/YOUR.DOMAIN.NAME/privkey.pem
Then run docker-compose up -d
Test
Test if it's working:
You can also utilize the built-in MiroTalk service by simply replacing YOUR.DOMAIN.NAME, your.username and your.password with your own values in the following URLs:
# Default listening port
https://p2p.mirotalk.com/icetest?iceServers=[{"urls":"stun:YOUR.DOMAIN.NAME:3478"},{"urls":"turn:YOUR.DOMAIN.NAME:3478","username":"your.username","credential":"your.password"}]
# TLS listening port
https://p2p.mirotalk.com/icetest?iceServers=[{"urls":"stuns:YOUR.DOMAIN.NAME:5349"},{"urls":"turns:YOUR.DOMAIN.NAME:5349","username":"your.username","credential":"your.password"}]
🔍 STUN vs. STUNS (the s suffix)
1. stun:
→ Plain STUN over UDP or TCP (no encryption).
- Default port: 3478
- Fastest and most widely supported.
- Used for discovering your public IP and NAT type.
- Works great when UDP is allowed.
2. stuns:
→ STUN over TLS (encrypted), typically on 5349 (or sometimes 443).
- Uses TLS similar to HTTPS for encryption.
- Useful in highly restricted networks or VPNs that block plain UDP.
- But: not all browsers and clients support
stuns:(especially older ones or mobile WebViews).